Forget Meat-free Monday
Meat free Mondays are a great idea, but opting to limit meat consumption to Sundays, with occasional extended breaks, can significantly reduce overall meat intake.
The approach emphasizes a diet rich in lentils paired with vegetables, reserving meat for Sundays. For instance, a Moroccan-inspired lamb stew shared among three individuals yesterday, complemented by vegetables, beans, and pulses, offered a delightful culinary experience.

The problem with food production
- 14.5% of global greenhouse gases originate from livestock.
- Deforestation primarily stems from agricultural activities.
- Water shortages are both caused by and affect farming practices.
- Ocean dead zones result from fertilizer runoff from large-scale agriculture.
The EAT-Lancet Commission report suggests that altering food production practices could reduce agricultural greenhouse gas emissions by approximately 10% by 2050. However, transitioning to a predominantly plant-based diet could potentially slash emissions by up to 80%. Additionally, halving food waste could yield an extra 5% reduction.
What is a plant based diet?
A plant-based diet emphasizes beans, nuts, seeds, fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and cereal-based foods.
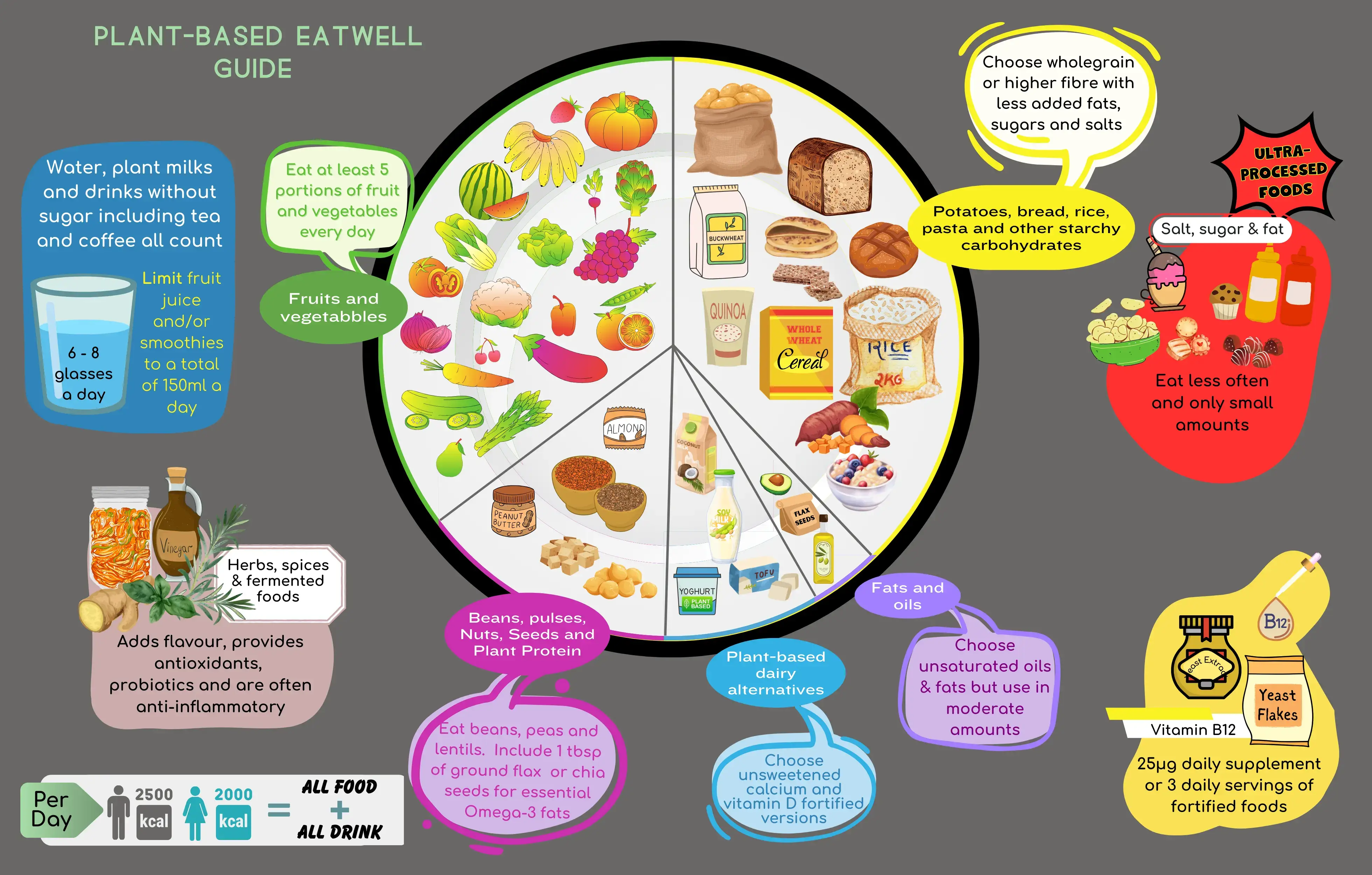
Health Benefits of a Plant-Based Diet
A well-balanced plant-based diet low in saturated fat offers various health advantages:
- Effective weight management.
- Reduced risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Lower risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Decreased risk of certain cancers.
It's essential to plan a plant-based diet properly, as with any other dietary regimen.
What can be done?
- Choose Seasonal Produce: Opt for seasonal produce to support local farmers and reduce energy-intensive practices like greenhouse farming and long-distance transportation.
- Practice Mindful Consumption: Be conscious of portion sizes to avoid overconsumption, thus reducing unnecessary food waste.
- Diversify Your Diet: Explore various plant-based foods to add diversity to meals and promote agricultural biodiversity.
- Reduce Single-Use Plastics: Minimize single-use plastics by utilizing reusable containers and bags while shopping or storing leftovers.
- Grow Your Own Food: Consider cultivating herbs, fruits, or vegetables at home to engage in sustainable food production.
- Support Sustainable Seafood: Choose seafood from sustainable sources with certifications like MSC or ASC to ensure environmental responsibility.
- Engage with Community Initiatives: Participate in local community gardens, farmer's markets, or food cooperatives promoting sustainable practices.
- Educate and Share Information: Spread awareness about sustainable eating practices and their environmental impact among friends and family.
- Embrace a Flexitarian Approach: Encourage occasional substitution of meat-based meals with plant-based options to reduce overall meat consumption.
- Advocate for Policy Change: Stay informed about food and agriculture policies and advocate for those supporting sustainability and reduced food waste.
Adopting a plant-based diet isn't solely about food; it's a strategy to align health and environmental well-being. Each meal choice represents a step toward fostering a sustainable future.